Basic Plotting Guide¶
The plotting tool in pyspeckit is intended to make publication-quality plots straightforward to produce.
For details on the various plotting tools, please see the examples and the
plotter documentation.
A few basic examples are shown in the snippet below, with comments describing the various steps. This example (https://github.com/jmangum/spectrumplot) shows how to use pyspeckit with spectral_cube to extract and label spectra. Other examples:
import numpy as np
from astropy import units as u
import pyspeckit
xaxis = np.linspace(-50,150,100.) * u.km/u.s
sigma = 10. * u.km/u.s
center = 50. * u.km/u.s
synth_data = np.exp(-(xaxis-center)**2/(sigma**2 * 2.))
# Add noise
stddev = 0.1
noise = np.random.randn(xaxis.size)*stddev
error = stddev*np.ones_like(synth_data)
data = noise+synth_data
# this will give a "blank header" warning, which is fine
sp = pyspeckit.Spectrum(data=data, error=error, xarr=xaxis,
unit=u.erg/u.s/u.cm**2/u.AA)
sp.plotter()
sp.plotter.savefig('basic_plot_example.png')
# Fit with automatic guesses
sp.specfit(fittype='gaussian')
# (this will produce a plot overlay showing the fit curve and values)
sp.plotter.savefig('basic_plot_example_withfit.png')
# Redo the overlay with no annotation
# remove both the legend and the model overlay
sp.specfit.clear()
# then re-plot the model without an annotation (legend)
sp.specfit.plot_fit(annotate=False)
sp.plotter.savefig('basic_plot_example_withfit_no_annotation.png')
# overlay another spectrum
# We use the 'synthetic' spectrum with no noise, then shift it by 10 km/s
sp2 = pyspeckit.Spectrum(data=synth_data, error=None, xarr=xaxis+10*u.km/u.s,
unit=u.erg/u.s/u.cm**2/u.AA)
# again, remove the overlaid model fit
sp.specfit.clear()
# to overplot, you need to tell the plotter which matplotlib axis to use and
# tell it not to clear the plot first
sp2.plotter(axis=sp.plotter.axis,
clear=False,
color='g')
# sp2.plotter and sp.plotter can both be used here (they refer to the same axis
# and figure now)
sp.plotter.savefig('basic_plot_example_with_second_spectrum_overlaid_in_green.png')
# the plot window will follow the last plotted spectrum's limits by default;
# that can be overridden with the xmin/xmax keywords
sp2.plotter(axis=sp.plotter.axis,
xmin=-100, xmax=200,
ymin=-0.5, ymax=1.5,
clear=False,
color='g')
sp.plotter.savefig('basic_plot_example_with_second_spectrum_overlaid_in_green_wider_limits.png')
# you can also offset the spectra and set different
# this time, we need to clear the axis first, then do a fresh overlay
# fresh plot
sp.plotter(clear=True)
# overlay, shifted down by 0.2 in y and with a wider linewidth
sp2.plotter(axis=sp.plotter.axis,
offset=-0.2,
clear=False,
color='r',
linewidth=2,
alpha=0.5,
)
# you can also modify the axis properties directly
sp.plotter.axis.set_ylim(-0.25, 1.1)
sp2.plotter.savefig('basic_plot_example_with_second_spectrum_offset_overlaid_in_red.png')
Basic plot example:
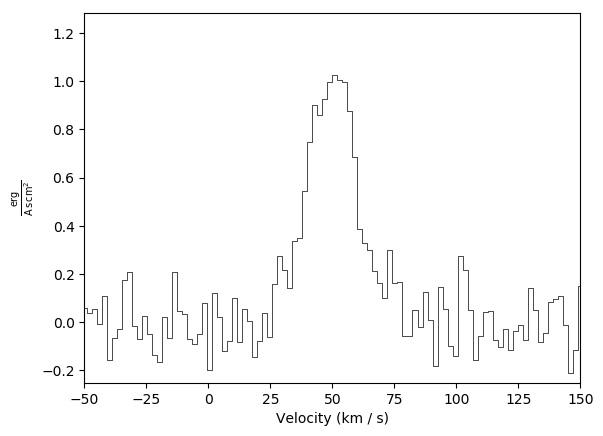
Basic plot example with a fit and an annotation (annotation is on by default):
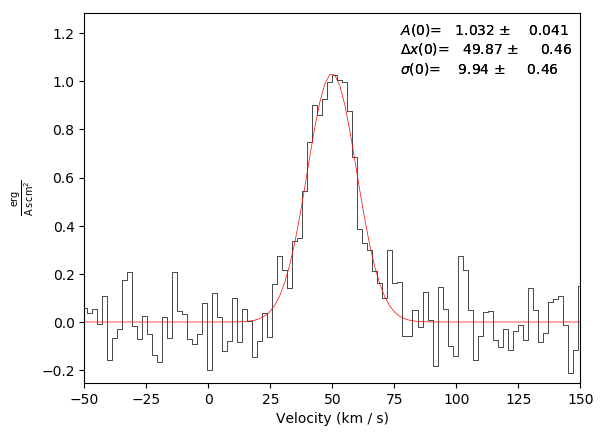
Basic plot example with a fit, but with no annotation:
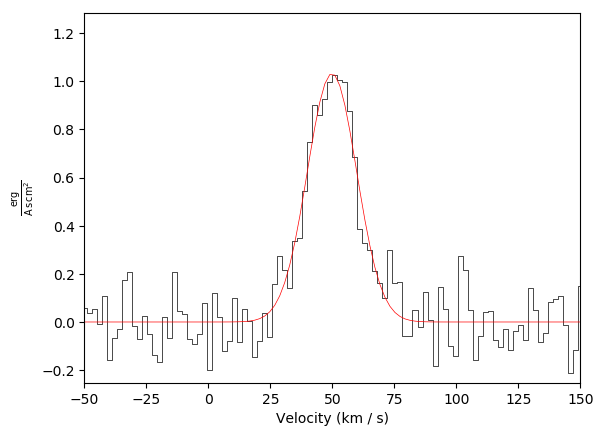
Basic plot example with a second spectrum overlaid in green:
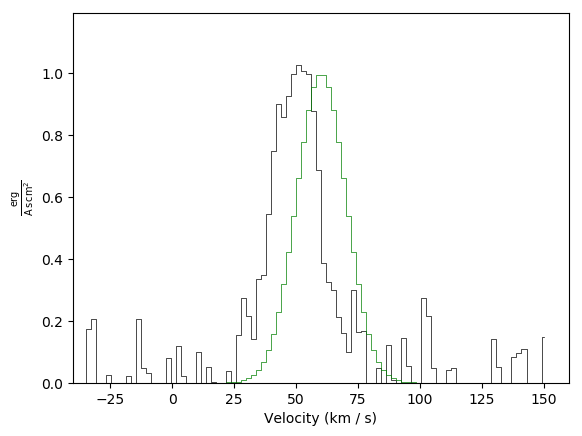
Basic plot example with a second spectrum overlaid in green plus adjusted limits:

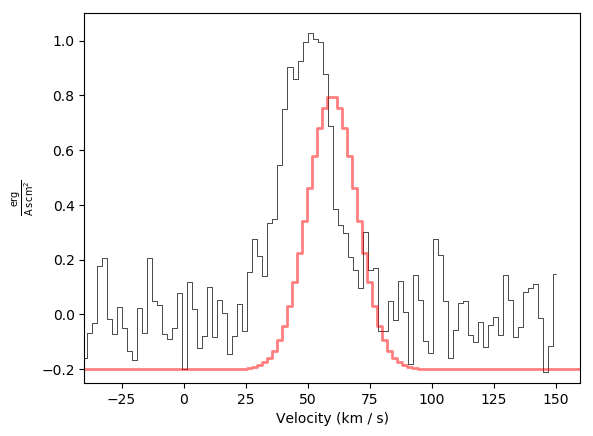
Basic plot example with a second spectrum offset and overlaid in red, again with adjusted limits:
API Documentation for Plotting¶
We include the API documentation for the generic model and fitter wrappers here.
- class pyspeckit.spectrum.plotters.BoundMethodProxy(meth, callback=None)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
- class pyspeckit.spectrum.plotters.Plotter(Spectrum, autorefresh=True, title='', xlabel=None, silent=True, plotscale=1.0, **kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Class to plot a spectrum
- activate_interactive_baseline_fitter(**kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Attempt to activate the interactive baseline fitter
- activate_interactive_fitter()[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Attempt to activate the interactive fitter
- connect()[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Connect to the matplotlib key-parsing interactivity
- copy(parent=None)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Create a copy of the plotter with blank (uninitialized) axis & figure
- [ parent ]
A spectroscopic axis instance that is the parent of the specfit instance. This needs to be specified at some point, but defaults to None to prevent overwriting a previous plot.
- disconnect()[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Disconnect the matplotlib interactivity of this pyspeckit plotter.
- label(title=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, verbose_label=False, **kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Label the plot, with an attempt to parse standard units into nice latex labels
- Parameters
title : str
xlabel : str
ylabel : str
verbose_label: bool :
- line_ids(line_names, line_xvals, xval_units=None, auto_yloc=True, velocity_offset=None, velocity_convention='radio', auto_yloc_fraction=0.9, **kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Add line ID labels to a plot using lineid_plot http://oneau.wordpress.com/2011/10/01/line-id-plot/ https://github.com/phn/lineid_plot http://packages.python.org/lineid_plot/
- Parameters
line_names : list
A list of strings to label the specified x-axis values
line_xvals : list
List of x-axis values (e.g., wavelengths) at which to label the lines. Can be a list of quantities.
xval_units : string
The unit of the line_xvals if they are not given as quantities
velocity_offset : quantity
A velocity offset to apply to the inputs if they are in frequency or wavelength units
velocity_convention : ‘radio’ or ‘optical’ or ‘doppler’
Used if the velocity offset is given
auto_yloc : bool
If set, overrides box_loc and arrow_tip (the vertical position of the lineid labels) in kwargs to be
auto_yloc_fractionof the plot rangeauto_yloc_fraction: float in range [0,1] :
The fraction of the plot (vertically) at which to place labels
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> import pyspeckit >>> sp = pyspeckit.Spectrum( xarr=pyspeckit.units.SpectroscopicAxis(np.linspace(-50,50,101), unit='km/s', refX=6562.8, refX_unit='angstrom'), data=np.random.randn(101), error=np.ones(101)) >>> sp.plotter() >>> sp.plotter.line_ids(['H$\alpha$'],[6562.8],xval_units='angstrom')
- line_ids_from_measurements(auto_yloc=True, auto_yloc_fraction=0.9, **kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Add line ID labels to a plot using lineid_plot http://oneau.wordpress.com/2011/10/01/line-id-plot/ https://github.com/phn/lineid_plot http://packages.python.org/lineid_plot/
- Parameters
auto_yloc : bool
If set, overrides box_loc and arrow_tip (the vertical position of the lineid labels) in kwargs to be
auto_yloc_fractionof the plot rangeauto_yloc_fraction: float in range [0,1] :
The fraction of the plot (vertically) at which to place labels
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> import pyspeckit >>> sp = pyspeckit.Spectrum( xarr=pyspeckit.units.SpectroscopicAxis(np.linspace(-50,50,101), units='km/s', refX=6562.8, refX_unit='angstroms'), data=np.random.randn(101), error=np.ones(101)) >>> sp.plotter() >>> sp.specfit(multifit=None, fittype='gaussian', guesses=[1,0,1]) # fitting noise.... >>> sp.measure() >>> sp.plotter.line_ids_from_measurements()
- parse_keys(event)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Parse key commands entered from the keyboard
- plot(offset=0.0, xoffset=0.0, color='k', drawstyle='steps-mid', linewidth=0.5, errstyle=None, erralpha=0.2, errcolor=None, silent=None, reset=True, refresh=True, use_window_limits=None, useOffset=False, **kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Plot the spectrum!
Tries to automatically find a reasonable plotting range if one is not set.
- Parameters
offset : float
vertical offset to add to the spectrum before plotting. Useful if you want to overlay multiple spectra on a single plot
xoffset: float :
An x-axis shift. I don’t know why you’d want this…
color : str
default to plotting spectrum in black
drawstyle : ‘steps-mid’ or str
‘steps-mid’ for histogram-style plotting. See matplotlib’s plot for more information
linewidth : float
Line width in pixels. Narrow lines are helpful when histo-plotting
errstyle : ‘fill’, ‘bars’, or None
can be “fill”, which draws partially transparent boxes around the data to show the error region, or “bars” which draws standard errorbars.
Nonewill display no errorbarsuseOffset : bool
Use offset-style X/Y coordinates (e.g., 1 + 1.483e10)? Defaults to False because these are usually quite annoying.
xmin/xmax/ymin/ymax : float
override defaults for plot range. Once set, these parameters are sticky (i.e., replotting will use the same ranges). Passed to
reset_limitsreset_[xy]limits : bool
Reset the limits to “sensible defaults”. Passed to
reset_limitsypeakscale : float
Scale up the Y maximum value. Useful to keep the annotations away from the data. Passed to
reset_limitsreset : bool
Reset the x/y axis limits? If set,
reset_limitswill be called.
- reset_limits(xmin=None, xmax=None, ymin=None, ymax=None, reset_xlimits=True, reset_ylimits=True, ypeakscale=1.2, silent=None, use_window_limits=False, **kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Automatically or manually reset the plot limits
- savefig(fname, bbox_inches='tight', **kwargs)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
simple wrapper of maplotlib’s savefig.
- set_limits_from_visible_window(debug=False)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Hopefully self-descriptive: set the x and y limits from the currently visible window (use this if you use the pan/zoom tools or manually change the limits)
- pyspeckit.spectrum.plotters.parse_norm(norm)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
Expected format: norm = 10E15
- pyspeckit.spectrum.plotters.steppify(arr, isX=False)[source] [github] [bitbucket]¶
support function Converts an array to double-length for step plotting
